本文介绍人脸识别算法,包括如何实现triplet代价函数,用训练好的模型将人脸图像映射为一个128维的编码向量,计算编码向量之间的距离实现人脸鉴定和人脸识别。
朴素人脸鉴定
人脸鉴定最直接的做法是对比两个图像之间的像素点,如果它们之间的距离小于某个选定的阈值,则判定为一个人。
这种算法性能很差,原因是:人脸的曝光度、朝向甚至是头部的位置稍微变化,像素值的变化就很大。
另一种更加稳健的做法,是先学习一个编码函数,然后再对比这个编码函数之间的差异,来判断是否为一个人。
1 | from keras.models import Sequential |
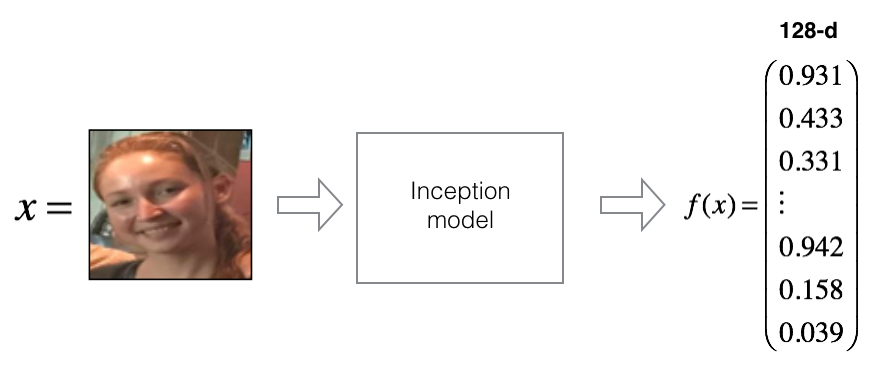
Using TensorFlow backend.将人脸图像编码为128维的向量
利用ConvNet计算编码函数
FaceNet模型需要大量数据和时间去训练,因此本文只加载训练好的模型。网络架构是Inception 模型Szegedy et al.。
需要注意的事项:
- 这个网络使用96*96的RGB图像作为输入,具体的说,输入图像集维度为:\((m, n_C, n_H, n_W) = (m, 3, 96, 96)\)。
- 输出编码函数的维度为\((m, 128)\)
1 | FRmodel = faceRecoModel(input_shape=(3, 96, 96)) |
1 | print("Total Params:", FRmodel.count_params()) |
Total Params: 3743280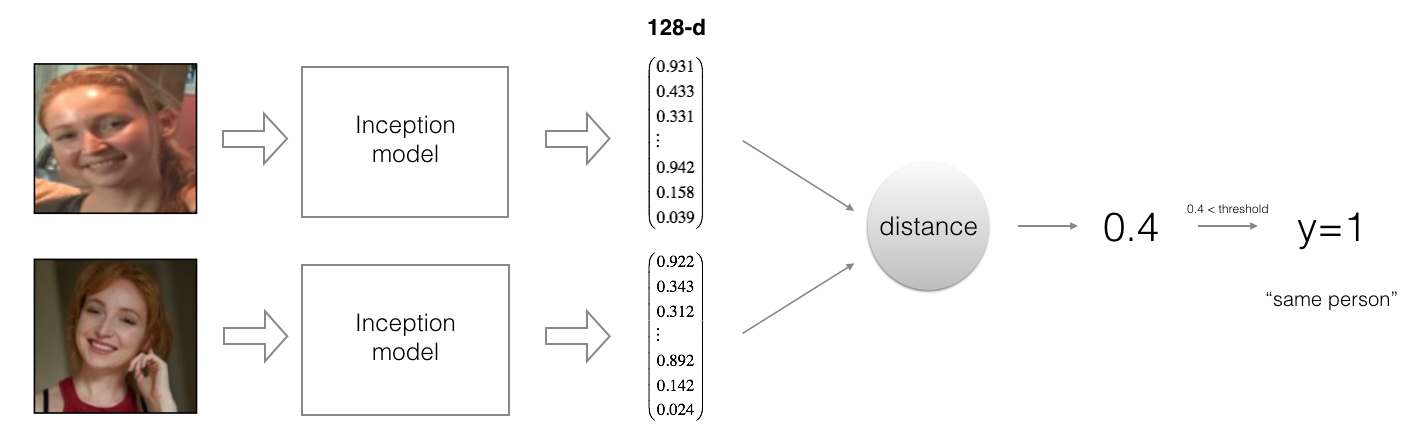
对比两个编码向量之间的距离,判断两张图片是否是一个人
判断一个编码是否好的条件:
- 同一个人的两张图片编码之后十分相似
- 不同人的两张图片编码之后差异很大
Triplet代价函数的目的就是实现这个功能,将同一个人的两张图片(Anchor和Positive)编码之后尽量推近,而将不同人的两张图片(Anchor和Negative)编码之后拉开。
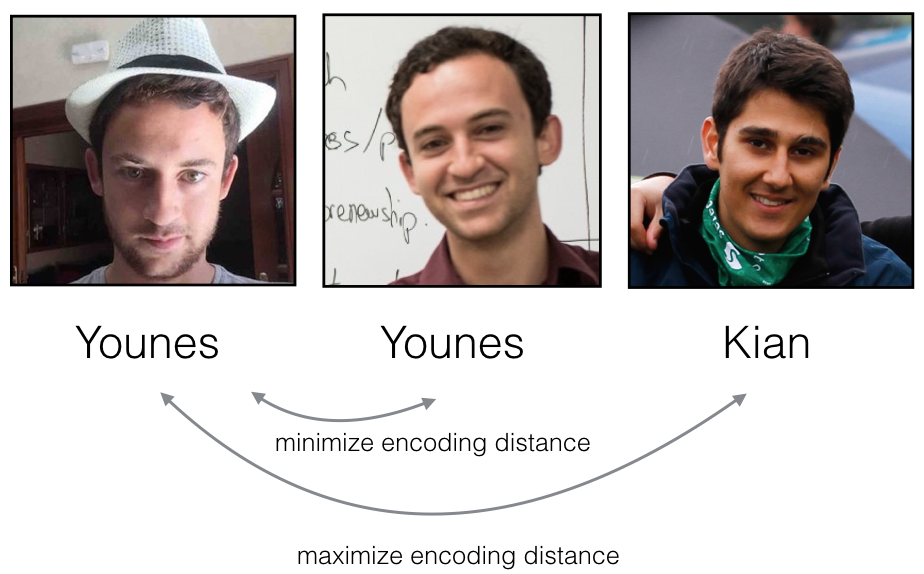
从左到右图片分别称为: Anchor (A), Positive (P), Negative (N)
Triplet代价函数
对一张图像\(x\), 其编码函数为\(f(x)\), 其中 \(f\) 为神经网络计算得到的函数。
训练过程使用三对图像 \((A, P, N)\):
- A 是 "Anchor" 图像--某个人的图像.
- P 是"Positive" 图像--和Anchor图像同一个人的图像.
- N 是"Negative" 图像--和Anchor图像不同人的图像.
这三对图像都是从训练数据集中提取出来的。\((A^{(i)}, P^{(i)}, N^{(i)})\) 表示第\(i\)个训练样本.
希望保证每一张图像 \(A^{(i)}\)和正图像 \(P^{(i)}\) 的距离至少比它和负图像之间 \(N^{(i)}\))之间的距离至少近 \(\alpha\)。
1 | # GRADED FUNCTION: triplet_loss |
1 | with tf.Session() as test: |
loss = 528.143加载训练好的模型
FaceNet模型最小化上面的triplet代价函数。由于需要大量数据和计算,本文加载已经训练好的模型。
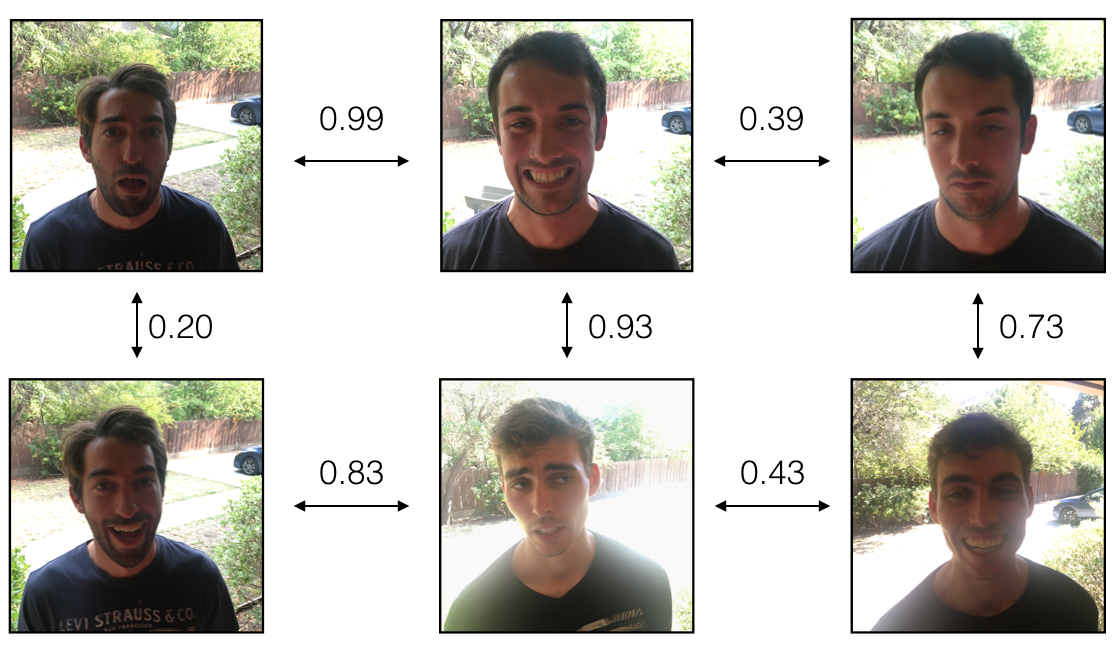

例子:计算三个人编码向量的距离
1 | FRmodel.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = triplet_loss, metrics = ['accuracy']) |
应用这个模型
人脸鉴定
将所有人的图像编码为128维向量,放在一个python字典中,组成数据库。当一个新成员进入,利用他输入的ID号,检查是否和数据库中这个人的编码向量是否匹配。
1 | database = {} |
1 | # GRADED FUNCTION: verify |
Younes试图进入开心屋,摄像头拍了一张他的照片,系统开始验证是否是Younes。

1 | verify("images/camera_0.jpg", "younes", database, FRmodel) |
It's younes, welcome home!
(0.65939283, True)Benoit破坏了开心屋的规则,偷了Kian的ID卡,试图假装成Kian混进开心屋。门前摄像头拍了一张他的照片,系统开始验证他是否是Kian。

1 | verify("images/camera_2.jpg", "kian", database, FRmodel) |
It's not kian, please go away
(0.86224014, False)人脸识别
和前面的人脸鉴定不同,这是1-k问题。流程如下:
- 计算新人图像的编码向量
- 从数据库中找到和新人图像距离最小的图像。
1 | # GRADED FUNCTION: who_is_it |
1 | who_is_it("images/camera_0.jpg", database, FRmodel) |
it's younes, the distance is 0.659393
(0.65939283, 'younes')结论及讨论
结论:
- 人脸鉴定解决的是1:1匹配问题;而人脸识别解决的是1:K匹配问题
- Triplet代价函数用于训练神经网络以学习人脸图像的编码函数,十分有效
- 相同的编码函数可以用于人脸鉴定和人脸识别。通过计算两张图像编码向量之间的距离,可以判断它们是否是一个人的图像
可以进一步改善算法性能的方面:
- 将每个人更多图像(不同的灯光、不同的角度等)的编码向量放入数据库中。给定新的图像,对比这张图像和这个人所有图像的编码函数,提高对比的精度
- 将图像剪切到只包含脸部,这种预处理手段可以消除脸部周围的不相关像素对算法的影响,提高算法的稳定性
参考资料
- 吴恩达,coursera深度学习课程
- Florian Schroff, Dmitry Kalenichenko, James Philbin (2015). FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering
- Yaniv Taigman, Ming Yang, Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, Lior Wolf (2014). DeepFace: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification
- The pretrained model we use is inspired by Victor Sy Wang's implementation and was loaded using his code: https://github.com/iwantooxxoox/Keras-OpenFace.
- Our implementation also took a lot of inspiration from the official FaceNet github repository: https://github.com/davidsandberg/facenet

